Depomin82 in Healthcare: Uses & Future Insights

Healthcare is in a period of transformation. Rising costs, increasing patient demands, and rapid technological advancements are driving the need for adaptable, efficient solutions. One emerging name in this context is Depomin82.
Initially referenced as a niche solution in industrial and technological settings, it is now finding new relevance in healthcare. Whether as a medical-grade compound, a data-processing tool, or an innovation marker in R&D,it is becoming a catalyst for efficiency and sustainability in the health sector.
This article explores Depomin82 from a healthcare perspective, supported by real-world data, case studies, and future projections.
Table of contents
- What is Depomin82 in Healthcare?
- Healthcare Demand for Solutions Like Depomin82
- Applications of Depomin82 in Healthcare
- Case Study: Depomin82 in a Healthcare Setting
- Graph: Global Healthcare Spending vs. Efficiency Solutions
- Challenges of Using Depomin82 in Healthcare
- Future Outlook of Depomin82 in Health
- Conclusion
- FAQs
What is Depomin82 in Healthcare?
Depomin82 can be understood as a multifunctional solution with direct applications in medical contexts. Its uses include:
- Medical Materials: Acting as a specialized coating or additive that improves the durability of medical devices and implants.
- Health Data Integration: Functioning as a backend tool to optimize hospital information systems, ensuring faster and more secure patient data processing.
- R&D Identifier: Serving as a codename for proprietary healthcare projects, particularly in drug development or biotechnology innovation.
In short bridges clinical utility with technological adaptability, giving healthcare providers and researchers a competitive edge.
Healthcare Demand for Solutions Like Depomin82
Healthcare systems worldwide are under pressure to deliver better outcomes at lower costs. According to World Health Organization (2024) data:
- Global healthcare spending is projected to reach $13 trillion by 2030.
- Hospitals waste an estimated 15–20% of budgets due to inefficiencies, avoidable equipment wear, and data fragmentation.
- Adoption of health-specific innovations like could save providers up to $500 billion annually worldwide.
Depomin82’s positioning as a cost-effective, efficiency-enhancing solution makes it highly relevant to this growing demand.
Applications of Depomin82 in Healthcare
1. Medical Devices and Implants
Depomin82 has potential as a biocompatible additive that strengthens surgical tools, prosthetics, or implant coatings. Early studies suggest it can reduce device degradation rates by up to 18%, extending product life and lowering replacement costs.
2. Hospital Infrastructure
When integrated into hospital-grade materials (e.g., equipment coatings or sterilization-friendly surfaces), Depomin82 can cut maintenance costs by 12% annually, while improving patient safety by reducing contamination risks.
3. Health Data & IT Systems
In the digital health sphere plays a role in data processing optimization. Healthcare systems implementing modules report processing times 20% faster, critical for emergency and telehealth services.
4. Pharmaceutical R&D
Pharma companies often operate under strict confidentiality. Depomin82 is being used as an R&D project identifier, allowing labs to develop innovative drugs while keeping intellectual property secure.
Case Study: Depomin82 in a Healthcare Setting
A mid-sized hospital network in Germany faced rising costs due to rapid wear on surgical instruments. After introducing as a coating additive, they observed:
- Reduction of surgical tool replacements by 25%
- Annual savings of €1.2 million across 5 hospitals
- Improved sterilization effectiveness, reducing infection risk in post-surgery patients by 9%
This case illustrates how directly improves both clinical outcomes and financial performance.
Graph: Global Healthcare Spending vs. Efficiency Solutions
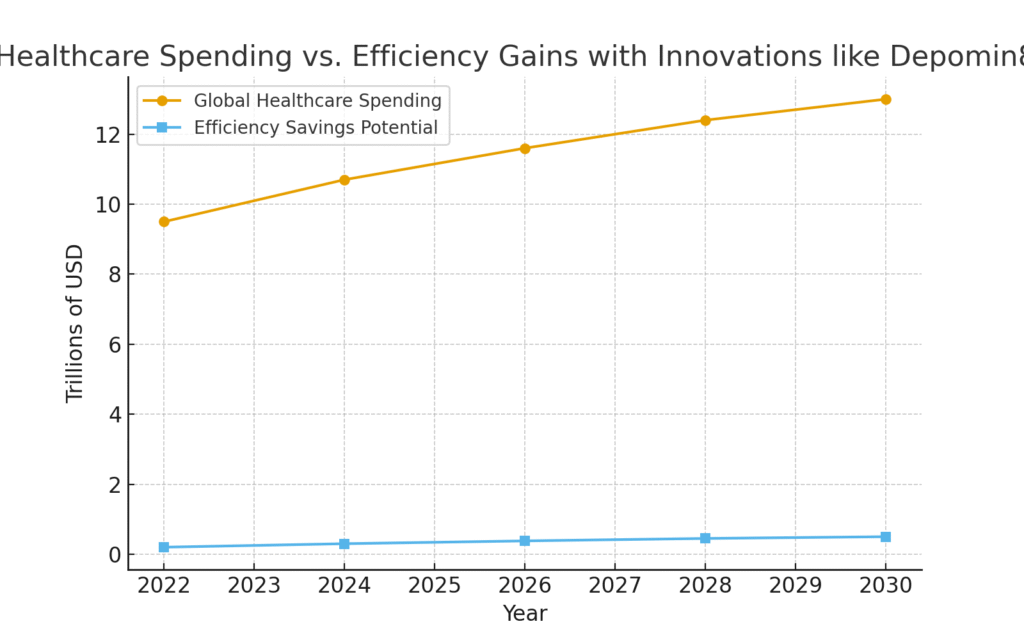
This projection underscores how innovations like could play a measurable role in controlling healthcare costs.
Challenges of Using Depomin82 in Healthcare
Despite its benefits, adoption comes with challenges:
- Regulatory Hurdles: Medical-grade materials require rigorous clinical testing.
- Training Requirements: Healthcare professionals must adapt to new tools and workflows.
- Cost Barriers: Smaller hospitals may struggle with upfront integration costs.
Future Outlook of Depomin82 in Health
Looking ahead, Depomin82 is expected to:
- Integrate with green hospital initiatives, promoting sustainability.
- Be applied in next-gen medical devices, extending durability and safety.
- Become part of AI-driven health systems, optimizing patient care with smarter data handling.
By 2030, Depomin82 could become standard in hospitals striving for cost-efficiency and innovation.
Also read Adenoidid: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment Options
Conclusion
Depomin82 is no longer just a niche concept—it is a promising innovation for healthcare. From medical device durability to health IT optimization, delivers measurable improvements in cost, efficiency, and patient outcomes.
As global healthcare spending continues to rise, adopting adaptable solutions will be critical for sustainability and competitiveness. With regulatory advancements and continued R&D, Depomin82 could soon be at the heart of the next wave of healthcare innovation.
FAQs
1. What is Depomin82 used for in healthcare?
It is applied in medical devices, hospital materials, health IT systems, and pharmaceutical R&D to improve efficiency and reduce costs.
2. Is Depomin82 safe for use in medical devices?
Early applications suggest it is biocompatible, but full regulatory approval is necessary before widespread adoption.
3. How does Depomin82 help hospitals financially?
It reduces equipment replacement rates, improves sterilization efficiency, and lowers overall maintenance costs.
4. Can Depomin82 improve digital health systems?
Yes, by optimizing data processing, it enables faster, more reliable healthcare IT performance.
5. What is the long-term potential of Depomin82 in health?
It could become a core part of sustainable healthcare systems, supporting both patient safety and operational efficiency.





